As recently as the early 1990s, most students did not take out college loans. Today roughly two out of every three students borrow to pay for college due to the runaway cost of college.
The typical student borrower is now leaving school with debt of roughly $35,000. Just the outstanding federal college loan debt now exceeds credit-card debt.
Keep this in mind – the level of debt will be more manageable if the student only borrows via federal student loans.
Federal Student Loans
For most students that will mean obtaining federal Direct Subsidized  Loans and Direct Unsubsidized Loans. You will also see them referred to as Stafford Loans, which is their old name.
Loans and Direct Unsubsidized Loans. You will also see them referred to as Stafford Loans, which is their old name.
Here is why these direct federal loans are superior:
- Students regardless of their income qualify for a direct federal loan if they are enrolled at least half time and complete the FAFSA.
- Students receive the same rates regardless of credit scores.
- The loans offer student repayment plans based on a grad’s current salary.
- The loans offer a public service student loan forgiveness program.
The federal Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans are designed strictly for students. Borrowers are expected to begin repaying these loans six months after graduating or leaving college.
Subsidized vs. Unsubsidized Loans
The interest rate on both the subsidized and the unsubsidized federal loans for the 2016-2017 school year is %, which is higher than the previous year’s rate of 3.76%. The interest rates are linked to the 10-year U.S. Treasury note.
The best loan to get is the Direct Subsidized Loan.
Students who qualify for the subsidized loan don’t have to pay the interest that accrues while they are enrolled in college. The federal government pays this interest. In contrast, students who borrowed via the Unsubsidized Direct Loan are responsible for covering the interest that accrues while in college.
Qualifying for a Direct Subsidized Loan
Your college will tell you if your child qualifies for the subsidized loan. Look at the financial aid package that your teenager receives to see what the breakdown is between subsidized versus unsubsidized loans.
A federal formula is used to determine if a student, based on a family’s finances, is eligible for the better subsidized deal. The majority of subsidized federal loans are awarded to students whose family’s adjusted gross income is less than $50,000.
You may see both kinds of Direct Loans in your package.
Federal Loan Borrowing Limits
Below you’ll find a federal chart that outlines how much students can borrow. The left-hand column shows the maximum amount that traditional (i.e. dependent) college students can borrow. Here is the definition of independent students.
The other column shows how much independent students , as well as dependent students whose parents were denied a federal PLUS Loan. Students whose parents could not obtain the PLUS Loan can borrow up to a total of $57,500.
If a student takes the traditional four years to graduate from college, the maximum he/she can borrow through Direct Loans will be $27,000. If the student needs longer to graduate with a bachelor’s degree he/she can only borrow an additional $4,000.

When to apply for a federal student loan
The new year for federal student loans starts July 1. So if your child will begin college in the fall, you would apply for the loan sometime after July 1.
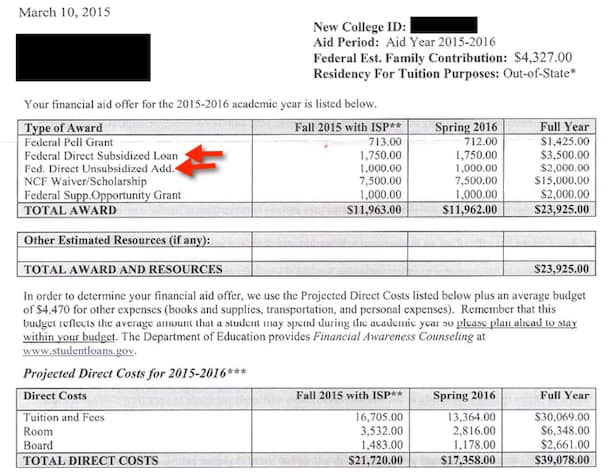
Your child’s school will notify you of the loan amounts that it is offering in an award letter. You can see in the example below how a college presents the two types of Direct Loans in a financial aid package.
You should evaluate the aid offer carefully. Keep in mind that whatever amount you borrow must be paid back with interest. If your living expenses are not as high as those projected by your school, you should not borrow as much as the amount in the award letter.
To get an idea of what monthly loan payments will be after graduation, take a look at the federal repayment calculator.
Perkins Loan – the other federal student loan
The second federal loan option for students is the Perkins Loan. Students who are eligible for the Perkins have what the federal government terms as exceptional financial need.
The interest rate for the Perkins is 5%.
With this loan, the student’s institution is the lender and borrowers make payments to their school or the institution’s loan servicer. If the money is available, the most a student is eligible to borrow is $5,500 a year.
Whether your child will qualify for the Perkins will depend, in part, on where he or she attends school. Because of the way the Perkin was established, not all schools can participate in the program and institutions that have access to more funds tend to be elite, private institutions.
Once a student has graduated, left school or dropped below half-time status, he or she has a nine-month grace period before Perkins payments must start.